A content audit is a systematic evaluation of all indexable content across your website to assess its SEO performance, user value, and strategic alignment with your brand’s goals. For SaaS companies, this means reviewing blog posts, product landing pages, feature announcements, help docs, and lifecycle content through a performance-first lens.
In 2025, content audits are not just about SEO hygiene. Conducting regular content audits of your website is now a necessity for LLM-based search visibility.
Platforms like Google SGE, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity extract and rank passages, not just URLs. That makes content structure, semantic clarity, and topical authority mission-critical.
🔎 According to Google Search Central, high-quality, helpful, and EEAT-aligned content is foundational for surfacing in AI-driven search experiences.
Without a regular content audit, SaaS sites risk housing duplicate, decayed, or cannibalized assets that dilute topical authority and confuse search systems (either human or AI).
▶️ Request Your Custom SaaS Content Audit Strategy
▶️ Best Tools for Tracking Brand Visibility in AI Search Platforms
Table of Contents
- What does a content audit include for SaaS websites?
- How do you perform a step-by-step SaaS-Focused content audit?
- What tools help you audit blog content?
- How do you find outdated or underperforming content on your site? Diagnostic Checklist
- How do you run a content audit using Google Search Console and GA4?
- Frameworks and tools for blog audit execution
- Signs your content is underperforming
- KPIs that matter in a SaaS content audit
What does a content audit include for SaaS websites?
A SaaS-specific content audit goes beyond surface-level SEO checks. It focuses on content types unique to software businesses and evaluates both marketing performance and product relevance.
Key elements in a SaaS content audit:
- Page-Type Classification (e.g., blog, feature page, comparison, glossary, support)
- Performance Metrics (organic traffic, conversions, dwell time, scroll depth)
- Keyword Relevance (match to ICP pain points and current queries)
- Semantic Structure (headings, FAQs, schema markup)
- Content Health Signals (recency, duplication, thinness, authoritativeness)
- Internal Linking & Topical Clustering (pillar-support structure validation)
- Conversion Path Mapping (is content aligned with product-led growth goals?)
Example: A feature blog post on “API integration workflows” may rank well, but be outdated in describing your current offering. A content audit flags this for refresh or deprecation.
Why are content audits important for LLM-based search systems like SGE?
Large Language Model (LLM) search systems such as SGE, Perplexity, and ChatGPT Browse don’t rank based solely on page-level authority. They extract meaning from semantically clear passages, reward well-structured chunks, and favor EEAT-aligned insights.
That means your site can have 1,000 blog posts, but if none of them are:
- Structurally modular
- Schema-enhanced
- Cited with authoritative references
- Internally cohesive with clear semantic clusters
…they likely won’t appear in AI-driven results.
The unit of optimization has shifted from pages to passages. AI systems extract and cite individual paragraphs or sections that support specific reasoning steps, regardless of overall page authority. (source)
Performing a content audit helps prepare your content for zero-click answers, AI-powered snippets, and RAG-based retrieval (all core to modern search UX).
How often should you perform a blog content audit?
For SaaS teams operating in competitive or rapidly evolving verticals, a quarterly content audit cycle is ideal. Here’s a scalable cadence model:
- Quarterly: Light-touch audit of all blog + key conversion pages
- Bi-annually: Full-scale audit with scoring, pruning, and re-optimization
- Monthly: Rolling review of new content performance (using GA4 & GSC)
The reason we suggest quarterly content audits is that SaaS products change rapidly due to feature launches, pricing changes, and GTM pivots, which can render blog content obsolete in just weeks.
What’s the difference between a content audit and an SEO audit?
While they often overlap, content audits and SEO audits serve different strategic purposes.
| Element | Content Audit | SEO Audit | Technical Audit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content quality, performance, alignment | On-page SEO, link signals, keyword optimization | Site speed, indexability, crawl issues |
| Tools | GSC, GA4, Ahrefs, manual review | Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, Screaming Frog | Google Search Console, Sitebulb, Screaming Frog |
| Use Cases | Refresh, prune, rewrite, republish | Improve rankings, address keyword gaps | Fix crawl errors, page speed, UX issues |
| LLM Readiness Factor | High (impacts passage extraction and surfacing) | Medium (aids discoverability and linking) | Indirect (impacts UX and accessibility) |
For SaaS companies preparing for AI-driven search, the content audit is now the primary driver of visibility and authority (especially for complex, mid-funnel, and product education content).
How do you perform a step-by-step SaaS-focused content audit?
This section introduces the operational process of executing a SaaS-specific content audit. It walks through inventorying pages, pulling data from GA4 and GSC, benchmarking performance, scoring with the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™, and assigning clear next actions (all structured for modern search readiness).
1. Inventory Your Existing Content
Use a crawler like Screaming Frog or export from your CMS to generate a URL-level content list. Filter only indexable, content-driven pages (exclude utility and legal pages).
💡 Pro Tip: Tag each entry by content type (e.g., “feature blog post,” “integration page”) in Excel or Notion or Airtable for easier filtering downstream.
2. Pull Performance Data from GA4 and Google Search Console
Match each URL to traffic, engagement, and query data:
- GA4: Sessions, average engagement time, conversions
- GSC: Impressions, CTR, average position, click-through by query
Combine into a master content performance table (CSV or Notion database).
3. Benchmark Against Your SEO and Business Goals
Create threshold markers:
- Under 100 organic sessions in 90 days = potential low performer
- Time on page < 45s = weak engagement
- No conversions in 180 days = low business value
4. Score Each Page Using the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™
Content pruning is the process of systematically removing, consolidating, or redirecting low-value content to improve overall site performance. In SaaS, this often includes old feature announcements, thin blog posts, and outdated comparison pages that no longer align with product or ICP priorities.
The SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™ (2x2 Model)
To decide what stays and what goes, apply this scoring model to every URL:
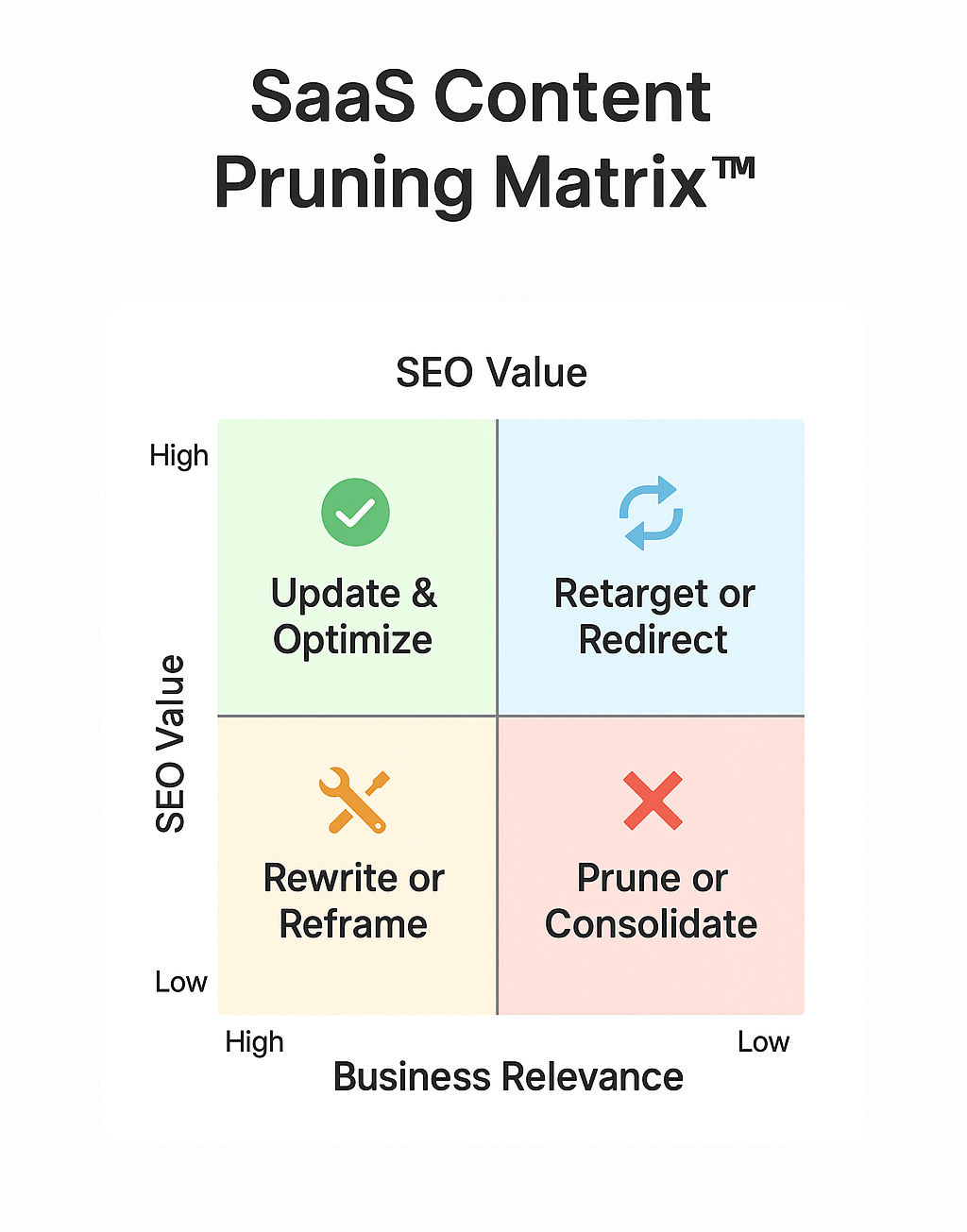
| Element | High Business Relevance | Low Business Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| High SEO Value | 🔄 Update & Optimize | 📈 Retarget or Redirect |
| Low SEO Value | 🛠 Rewrite or Reframe | 🗑 Prune or Consolidate |
Pages in the “Low SEO / Low Business” quadrant are pruning priorities. These create noise for users, dilute crawl equity, and rarely result in conversions.
⚠️ Example: A 2018 post about a deprecated integration that gets <20 organic sessions per quarter—low relevance, low reach. Ideal pruning candidate.
Pro Tip: Use GA4 and GSC to filter pages with:
- <100 sessions in 90 days
- 0 conversions
- No backlinks or ranking terms
Pruning these frees up crawl budget, sharpens topical authority, and lets high-impact pages shine.
5. Identify Content Opportunities and Risks
- Content Cannibalization: Look for URLs targeting the same intent (Ahrefs → Site Audit → Keyword Overlap)
- Thin Content: <300 words or lacking topical depth
- Outdated Posts: Features, screenshots, or pricing no longer accurate
6. Tag for Action: Update, Merge, Delete, Keep
Use a column in your Airtable or Notion board to assign actions:
- 🟩 Keep = performing and current
- 🟨 Update = accurate but stale or under-optimized
- 🟧 Merge = duplicate or cannibalizing topic
- 🟥 Delete = no SEO or business value
7. Document Recommendations and Assign Ownership
Create an “Content Audit Summary” report that includes:
- Top priority actions (with URL, action type, rationale)
- Owner assignments (editor, SEO lead, designer)
- Update queue synced to your content calendar
8. Track Post-Audit Performance
Re-measure key metrics 30–60–90 days after changes:
- Rank shifts (via Ahrefs or GSC)
- CTR changes
- Traffic delta
- Conversion lift
What tools help you audit blog content?
Recommended tool stack for saas content audits:
| Tool | Use Case | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Screaming Frog | Crawl your site and export all indexable URLs, metadata, word counts, canonical tags | Forms the foundation of your audit inventory |
| Google Search Console (GSC) | Track keyword rankings, impressions, CTR, and indexing status | Surfaces what content Google sees and how it performs in real searches |
| GA4 (Google Analytics 4) | Review engagement time, scroll depth, bounce rate, and conversions | Connects SEO performance to actual user behavior and funnel value |
| Ahrefs | Detect content cannibalization, backlink data, keyword gaps | High-value tool for SEO signal strength and keyword overlap auditing |
| Clearscope / Surfer SEO | Optimize updated posts with semantic relevance to current ranking pages | Ensures refreshed content aligns with topical and keyword expectations |
| Notion or Airtable | Tag content by type, score with the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™, assign action status (update/delete/etc.) | Enables team workflows, ownership, and audit transparency |
| ChatGPT / Claude | Summarize old content, propose update angles, or rewrite metadata at scale | Accelerates the editing and ideation layer of large-scale updates |
🔄 Tools to Avoid (or Use with Caution)
- Yoast SEO scores: Surface-level signals, not reliable for content scoring
- Heatmaps (unless conversion is core goal): Add noise unless tied to clear actions
- Free audit checkers: Often generic and lack contextual depth for SaaS
How do you find outdated or underperforming content on your site? Diagnostic Checklist
Use this 5-part triage to flag content that may be hurting your SaaS blog’s SEO or UX performance.
1. Low Organic Traffic (GA4 + GSC)
- Page has <100 organic sessions in the last 90 days
- CTR is <0.5% with >500 impressions
- No traffic-driving queries in GSC’s Top 10
2. Decaying Rankings (GSC)
Use the GSC "Compare Dates Filter" view to identify:
- 🔻 Position drop >3 places over 60 days
- 🔻 Impression loss >30% on previously top keywords
- 🔻 Keywords slipping from Page 1 to Page 2+
💡 Tip: Export query-level position deltas to pinpoint which terms are eroding.
3. Thin or Outdated Content
- Under 300 words or lacking visual/supporting assets
- Mentions deprecated product features or legacy screenshots
- Last modified date is >12 months ago with no update log
Use Screaming Frog’s “Last Modified” filter or CMS export metadata to batch identify old content.
4. No Conversions or Bottom-Funnel Impact
- Zero demo clicks, trial signups, or scroll-to-CTA activity in GA4
- Bounce rate >85% with <20% scroll depth
For SaaS, content must move the funnel, not just rank.
5. Keyword Cannibalization or Redundancy
Run a keyword overlap report in Ahrefs:
- Two or more pages rank for the same cluster with volatile positions
- Both underperform vs competitors
How do you run a content audit using Google Search Console and GA4?
Pairing Google Search Console (GSC) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) enables a full-funnel view of how your content ranks, engages, and converts. This section provides a tactical walkthrough for using both tools to diagnose underperformance and prioritize optimizations.
Running a Content Audit with GSC + GA4: 6 Tactical Steps
Pairing Google Search Console (GSC) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) enables a full-funnel view of how your content ranks, engages, and converts.
Here's how to use both platforms in tandem for a SaaS-focused audit.
1. Export All Indexable URLs for Analysis
Use Screaming Frog, your CMS, or GSC → Pages tab to export all indexable content URLs. Filter out:
- Legal pages
- Non-indexed URLs
- Redirects or 404s
💡 Pro Tip: In GSC, go to: Performance → Pages → Export → Last 3 Months
2. Pull Search Performance Data from GSC
For each URL, collect:
- Total Clicks
- Total Impressions
- Average CTR
- Average Position
- Top Queries (per page)
⚠️ Red Flag Patterns:
- CTR < 0.5% with >1,000 impressions = likely misalignment with intent
- Position drop >3 places in last 60 days = possible content decay
3. Segment Queries to Find Opportunity Gaps
Use GSC's "Queries" tab for each URL:
- Look for keywords ranking on Page 2 (positions 11–20)
- Identify keywords with high impressions but low clicks
- Export and group by intent: navigational, informational, transactional
- Add this to your content update strategy: improve targeting, meta descriptions, or internal linking.
4. Connect GA4 for Engagement + Conversion Metrics
Go to GA4 → Reports → Engagement → Pages and Screens. For each URL, gather:
- Users / Sessions
- Average Engagement Time
- Bounce Rate / Scroll Depth
- Event Completions (e.g., CTA clicks, demo form fills)
⚠️ Audit Triggers:
- Engagement Time < 45s
- Scroll Depth < 25%
- No conversions over 90 days
5. Join GSC and GA4 Data in a Master Sheet
Create a centralized audit sheet with:
- URL
- SEO metrics (GSC)
- UX + Conversion metrics (GA4)
- Action tag (Update, Keep, Delete)
- Notes and recommendations
Use Notion, Airtable, or Google Sheets with filters to enable content audit workflows.
6. Prioritize Based on Combined Signals
Sort by:
- Low CTR + High Impression
- High Engagement but Low Rank
- Good Rank but No Conversions
These hybrid insights reveal:
- Content that ranks but doesn’t convert
- Posts that attract traffic but offer poor UX
- Pages close to Page 1 that need minor tweaks
💡 Pro Tip: Set up Looker Studio dashboards with GSC + GA4 connectors for live audit views across teams.
Frameworks and Tools for Blog Audit Execution
This section introduces decision-making structures (like the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™ and RICE) and tools (from Notion to Ahrefs) that agencies and in-house teams rely on to audit content at scale.
What frameworks are best for SaaS content audits?
For SaaS blogs aiming to rank in LLM-driven search results (like Google SGE or Perplexity), a solid audit framework isn’t just helpful, it’s non-negotiable. The right model helps you score content by both business value and SEO performance, so you can confidently prune, optimize, or expand based on strategic impact.
Recommended Frameworks for SaaS Content Audits:
| Framework | Best For | Structure | Pros | Watchouts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™ | Mid-to-large SaaS blogs | 2x2 matrix (SEO Performance vs Business Value) | Easy prioritization for pruning vs updating; aligns with revenue goals | Requires traffic + conversion data for full use |
| Content Lifecycle Audit | Growth-stage teams scaling ops | Time-based checkpoints (Create → Promote → Audit → Sunset) | Supports quarterly content ops; good for recurring systems | Can delay fast pruning decisions |
| Pillar-Cluster Mapping | Feature-driven SaaS blogs | Topic graph linking core pages to blog content | Surfaces cannibalization and topical gaps | Requires strong internal linking hygiene |
| RICE Scoring for Content | Teams with limited resources | RICE = Reach × Impact × Confidence ÷ Effort | Forces objective decisions; good for backlog triage | Risk of over-indexing on “effort” and under-pruning |
Content audits provide a structured framework for evaluating the performance of your content. Start by reviewing data on traffic, engagement, and conversions and identify which pieces of content are delivering value and which may need attention. (source)
What’s the difference between manual vs automated content audits?
Choosing between manual and automated content audits depends on your team’s size, data literacy, and the scale of your SaaS blog. Here’s how the two approaches compare and when to use each.
Manual vs Automated Content Audits: Comparison Matrix
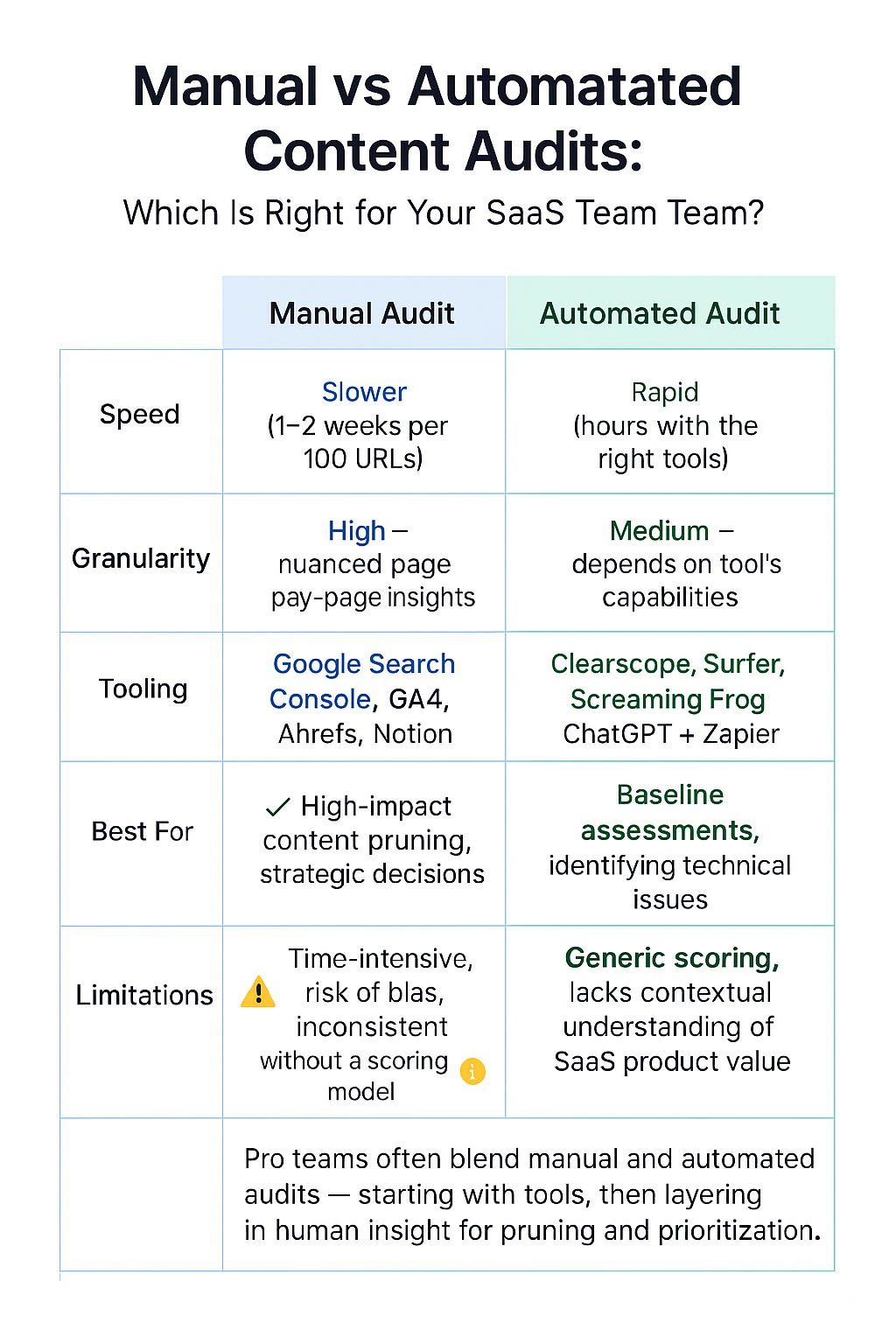
| Category | Manual Audit | Automated Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower (1–2 weeks per 100 URLs) | Rapid (hours with the right tools) |
| Granularity | High — nuanced page-by-page insights | Medium — depends on tool’s capabilities |
| Tooling | Google Search Console, GA4, Ahrefs, Notion | Clearscope, Surfer, Screaming Frog, ChatGPT + Zapier |
| Best For | High-impact content pruning, strategic decisions | Baseline assessments, identifying technical issues |
| Limitations | Time-intensive, risk of bias, inconsistent without a scoring model | Generic scoring, lacks contextual understanding of SaaS product value |
When to Use Manual Content Audits?
- You’re pruning mission-critical blog content tied to product features or sales.
- You need human judgment on tone, depth, and intent alignment.
- You're applying a custom scoring matrix like the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™.
When to Use Automated Content Audits?
- You're identifying thin content, 404s, duplicate URLs, or cannibalization at scale.
- You want to tag and cluster content for bulk actions (e.g., “low-performing, high-traffic”).
- You're feeding data into a Notion or Airtable dashboard for ongoing optimization.
Automated audits flag surface‑level errors, but humans understand context, intent, and strategy. The best approach? Leverage AI for scale and humans for strategic insights. (source)
Should you use AI tools or SEO platforms for auditing?
Choosing between AI tools and traditional SEO platforms depends on your audit goal: semantic tagging, performance analysis, or content decisioning. Each category excels differently and in 2025, hybrid use is often best.
AI Tools vs SEO Platforms: Key Differences
| Tool Type | Best For | Examples | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Assistants (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude) | Semantic audits, topic tagging, summary generation | ChatGPT-4o, Claude 3.5 | Speed at scale, contextual analysis, automated rewrite suggestions | Requires human validation; lacks first-party traffic data |
| SEO Platforms (e.g., Clearscope, Surfer, Ahrefs) | Performance audits, keyword gap analysis, optimization scoring | Clearscope, Surfer SEO, Ahrefs, SEMrush | Empirical data, SERP analysis, keyword scoring | Can miss semantic nuance or content purpose |
| Hybrid Workflows | Teams needing both data + context | ChatGPT + Ahrefs + Notion tagging | Combines strengths of both AI and data tools | More setup; needs a documented workflow |
When to use which:
- Use AI tools if… you're auditing semantic relevance, clustering content by intent, or accelerating content brief creation.
- Use SEO platforms if… you're diagnosing ranking drops, traffic declines, or keyword opportunities with hard data.
- Use both if… you're performing a strategic SaaS blog overhaul where both technical signals and narrative alignment matter.
How do content audit approaches differ for blogs vs landing pages?
Blog audits and landing page audits serve different strategic purposes, and your audit methodology must reflect that. While blog content is evaluated for its topical depth, freshness, and internal SEO role, landing pages are audited primarily for conversion rate and commercial alignment.
Key Differences in Content Audit Approach For Blogs & Landing Pages
| Element | Blog Content Audit | Landing Page Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Topical authority, traffic growth, internal linking | Conversion rate, lead generation, product alignment |
| Audit Frequency | Quarterly or bi-annual | Trigger-based (after product updates, CRO sprints) |
| SEO Signals Prioritized | Content freshness, keyword coverage, CTR | Meta clarity, URL structure, load speed |
| Tooling Emphasis | GA4, GSC, Clearscope, Ahrefs | Hotjar, Google Optimize, Unbounce, CRO tools |
| Scoring Criteria | SEO traffic, engagement depth, update opportunity | Conversion rate, time to form-fill, CTA performance |
💡 If-Then Guidance:
- If your blog post isn’t driving organic traffic or linking internally to product pages, it needs content scoring and pruning.
- If your landing page has traffic but no conversions, start with CRO-focused audits: test CTAs, value props, and layout.
What are the top content audit templates used by agencies?
Top-tier SaaS SEO agencies don’t start audits from scratch. They deploy proven templates to standardize decision-making, speed up execution, and align stakeholders. The best templates blend technical SEO indicators, content quality heuristics, and business impact scoring.
Here are the most commonly used (and agency-tested) templates in SaaS content audits:
Top Content Audit Templates Used by Agencies
1. URL-Level Content Inventory Spreadsheet
- Format: Google Sheets or Airtable
- Fields: URL, Title, Word Count, Last Updated, Organic Traffic, GSC Clicks, Target Keyword, CTA Presence
- Best For: Full blog sweeps and pruning analysis
💡 Pro Tip: Use conditional formatting to surface zero-click or outdated pages at a glance.
2. Content Scorecard Template
- Structure: Weighted scoring system (e.g., 1–5 scale)
- Criteria: SEO traffic, backlink equity, engagement, conversion relevance, brand alignment
- Best For: Stakeholder presentations; easy yes/no decisions
- Agency Use: Often built in Notion or Airtable to support filtering/tagging workflows.
3. Content Action Matrix
- Framework: 4 action tags — Keep, Update, Merge, Remove
- Best For: Quick prioritization of blog portfolios
- EEAT Boost: When paired with metadata (author, schema, publish date), this becomes SGE-audit ready.
4. SERP Coverage Gap Template
- Tool: Often used alongside Ahrefs, Semrush, or Clearscope
- Fields: Query, Ranking Page, Competitor URL, Intent Match, Refresh Opportunity
- Best For: Top-of-funnel or thought leadership content
- Agency Insight: Helps identify clusters where you’re absent or misaligned on search intent.
5. Audit Tracker with Status & Owner Columns
- Format: Airtable, Notion, or ClickUp
- Best For: Managing live updates in collaborative content ops
- Example Columns: Audit Status, Assigned Owner, Last Review Date, Notes/Next Action
At top B2B SEO agencies, these templates aren’t used in isolation. They’re stitched together into a unified audit dashboard with pivot views for content strategists, SEOs, and marketing execs. This ensures alignment across ops, SEO, and leadership.
Content audits help you assess objectively how well your content meets your audience needs… Typically, 5 % of content generates 90 % of all engagement. The content audit gets you to your 5 %. (source)
Signs Your Content Is Underperforming
This section teaches SaaS teams how to spot decaying performance using concrete patterns in GA4 and GSC, like low CTR, declining rankings, or bounce-heavy UX signals, to triage what needs pruning or refresh.
How do I know if my content is outdated or hurting SEO?
Outdated or underperforming content doesn’t always announce itself, but certain data signals in GSC and GA4 serve as clear indicators. If these patterns (discussed below) emerge, the content may be harming your site’s SEO performance rather than helping it.
| Symptom | Where to Look | What It Suggests |
|---|---|---|
| CTR < 1% on queries with high impressions | GSC → Performance → Pages | Meta title/description is stale or mismatched with intent |
| Position drop > 5 in < 60 days | GSC → Query/URL view | Algorithmic decay, new competitors, or neglected updates |
| 0 clicks with > 500 impressions in 90 days | GSC → Queries tab | Likely intent mismatch or low topical authority |
| Avg. time on page < 30 sec | GA4 → Engagement metrics | Thin content or poor content-format match |
| Pages with < 100 organic sessions in 90 days | GA4 → Pages & screens | Likely underindexed, irrelevant, or duplicate content |
💡 Pro Tip: Set a GSC filter for "Last 3 months" vs "Previous 3 months" to visualize traffic decay over time.
Quick Content Diagnostic Checklist
- Page dropped out of top 20 for primary keyword?
- CTR underperforming despite stable rankings?
- No backlinks earned since publication?
- Low scroll depth or bounce rate > 85%?
- Competing internal pages ranking for the same term?
If you check 2+ of these boxes, the page likely needs a content refresh, consolidation, or deindexing as part of a content pruning workflow.
What are signs of decaying content performance?
Content decay refers to the gradual decline in a page’s organic visibility over time. This is usually due to algorithm updates, better competing content, or topical obsolescence. Unlike sudden traffic drops, decay is subtle but diagnosable with trend comparison in Google Search Console.
Visual Content Decay Example (GSC View)
| Metric (GSC) | Last 3 Months | Previous 3 Months | Change | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impressions | 8,220 | 12,450 | ↓34% | Visibility decline likely due to lost keyword coverage |
| Clicks | 540 | 1,030 | ↓47% | Sharp CTR drop indicates decaying relevance or competition |
| Avg. Position | 18.3 | 11.2 | ↓7.1 | Moved off Page 1—time for re-optimization |
Key Signs of Content Decay
- Rank Drift: A slow but steady drop in average position across top queries
- Impression Fade: Fewer query exposures despite same page and topic
- CTR Deterioration: Ranking remains stable, but users stop clicking
- Lost Featured Snippets or Sitelinks: Indicates reduced authority or relevancy
- Search Query Change: Your page no longer aligns with how users phrase the query
Why do SaaS blogs lose organic traffic over time?
Organic traffic erosion in SaaS blogs is rarely random. It usually follows a predictable set of causes rooted in how algorithms reward freshness, relevance, and authority. Without structured audits, content degradation becomes inevitable.
Core Causes of Traffic Decline in SaaS Blogs
- Algorithmic Freshness Bias: Google favors recently updated or newly published content for competitive keywords. Evergreen posts stagnate unless refreshed regularly.
- Query Drift: The way users phrase search queries evolves. A blog titled “How to Manage Customer Onboarding in 2022” may not match the 2025 search intent of “AI onboarding tools for SaaS.”
- Internal Competition (Keyword Cannibalization): Multiple blog posts targeting similar terms (e.g., "customer onboarding checklist" vs "how to improve SaaS onboarding") compete for the same SERP, diluting rankings.
- Competitor Leapfrogging: New players with better structured content or integrated schema can overtake once-dominant legacy pages.
- Link & Engagement Decay: Older posts that no longer earn backlinks or traffic signals lose ranking power. This especially affects middle- and bottom-of-funnel content in SaaS blogs.
Recommended Practice
Build decay-mitigation into your content ops:
- Quarterly refresh cycles for posts older than 12 months
- Use GSC to track rank delta on core URLs
- Prune or consolidate cannibalizing pages quarterly
How do I identify thin, duplicate, or irrelevant content?
Low-value content quietly drags down your overall site authority and dilutes crawl equity. Identifying it is a mix of data review, content mapping, and judgment. Use this triage approach during a content audit.
| Issue Type | Symptoms | How to Detect | Tool Suggestions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thin Content | <300 words, poor dwell time, high bounce | Word count audit, GA4 time-on-page under 30s | Screaming Frog, GA4 |
| Duplicate Content | Same H1/meta across URLs, URL variations | Crawl duplication reports, canonical mismatches | Sitebulb, Ahrefs Site Audit |
| Irrelevant Content | Low topical alignment with product/ICP, no conversions | Manual audit, engagement < 0.5 pages/session | Airtable scoring, Hotjar for intent mismatch |
Thin or Irrelevant Content Checklist
- Content under 300 words with no images, examples, or internal links
- Page gets <100 organic sessions in 90 days and <0.5 average pages per session
- Doesn't match any ICP pain points or funnel stage
- Targets keywords unrelated to your current product offering
- No backlinks, no conversions, no engagement history
💡 Pro Tip: Content that brings no visits, links, engagement, or conversions (and isn't strategically useful) likely qualifies for pruning.
How do you uncover cannibalization or keyword overlap?
Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your site compete for the same query, splitting clicks, diluting authority, and confusing Google about which one should rank. This is especially common in SaaS blogs with overlapping use cases, guides, and feature content.
How to Diagnose Keyword Cannibalization?
Step 1: Query-to-URL Mapping in GSC
- Go to Google Search Console → Performance → Queries
- Click a key query (e.g., "customer onboarding SaaS")
- Check if multiple URLs appear under “Pages” tab for that query
If more than one URL shows meaningful impressions or clicks for the same query, you may have a cannibalization issue.
Step 2: Run Site-wide Query Export
- Use Ahrefs or GSC export to pull Top Queries per URL
- Sort and tag pages that rank for identical or semantically similar keywords
- Look for clusters: e.g., 4 posts ranking for variants of "churn reduction"
Step 3: Review SERP Intent and Content Type
- Check if content pieces are trying to solve the same problem with different formats (e.g., checklist, blog, landing page)
- If intent is similar but formats differ, consider consolidation or canonicalization
Common Overlap Scenarios in SaaS Blogs
- Multiple “How-To” guides on the same feature
- Old blog post and new product page targeting same keyword
- Industry roundup competing with evergreen guide on same term
- Blog FAQ stealing rankings from dedicated support content
KPIs That Matter in a SaaS Content Audit
This section focuses on the metrics that prove whether your content is working (before and after the audit). It breaks down essential KPIs like organic sessions, scroll depth, ranking volatility, and conversion attribution, all tied to audit impact evaluation.
What KPIs should you track during a content audit?
To measure the true impact of a SaaS content audit, prioritize metrics that signal performance, engagement, and conversion. These KPIs should help you evaluate both search visibility and bottom-line impact:
| Metric | Tool(s) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Traffic | GA4, GSC, Ahrefs | Indicates visibility; stable or increasing traffic signals healthy rankings. |
| Average Time on Page | GA4 | Low time may indicate misaligned intent or shallow content. |
| Scroll Depth | GA4 | Shows content engagement; high bounce + low scroll = UX or content mismatch. |
| Conversion Rate (Soft + Hard) | GA4 | Tie content to demo signups, free trials, or email captures. |
| Keyword Ranking Volatility | Ahrefs, SEMrush | Tracks fluctuations pre/post audit; stability = authority, volatility = risk. |
| Pages per Session | GA4 | SaaS blogs benchmark at 1.5–2.3; higher means stronger internal linking & value. |
| Backlinks Earned | Ahrefs | Reflects authority and potential for content to rank and attract new visitors. |
How do you measure content performance before and after an audit?
To assess the ROI of a content audit, use a before-and-after comparison window (typically 30, 60, or 90 days). Anchor your analysis around 5 core performance lenses, and apply consistent comparison logic.
Pre/Post-Audit Performance Checklist:
1. Traffic Delta (Organic Only)
- Tool: Google Search Console, GA4
- Check: % change in organic sessions for audited URLs
- If traffic increases >15%, the content updates improved visibility or intent-match.
2. Engagement Shift
- Tool: GA4 (avg. time on page, bounce rate, scroll depth via custom events)
- Check: Are users staying longer and scrolling deeper?
- If time on page ↑ + scroll depth ↑, content quality and UX have improved.
3. Ranking Movement
- Tool: Ahrefs, SEMrush
- Check: Monitor keyword position shifts for target pages
- If rankings climb into top 3 or page 1, the audit likely improved semantic alignment.
4. Conversion Attribution
- Tool: GA4 Goals
- Check: Did goal completions (trials, signups) increase from updated posts?
- If conversion-assisted sessions ↑, the audit improved funnel performance.
5. Content Velocity & Indexation
- Tool: GSC (Index Status, Coverage)
- Check: Faster indexing or crawl frequency post-update signals improved crawl efficiency
- If crawl rate ↑ or old content is reindexed, Google is re-evaluating page relevance.
What content types drive the best SEO ROI in SaaS?
In SaaS SEO, not all content types yield equal ROI. The top-performing formats balance search intent, buyer journey stage, and conversion potential. Through dozens of content audits across B2B SaaS sites, the following content types consistently show the highest SEO-to-pipeline impact:
High-ROI SaaS Content Types
- Bottom-of-Funnel Comparison Pages (E.g., “Tool A vs Tool B” or “Best [Category] Tools”)
- High conversion intent
- Often rank for commercial queries with SERP features (FAQs, review snippets)
- “What Is” and Definition Content (E.g., “What is SOC 2 Compliance?”)
- Capture top-of-funnel traffic with high linkability
- Frequently pulled into SGE snapshots and featured snippets
- Perfect for internal linking to gated content or case studies
- Solution-Aware Use Case Posts (E.g., “How to Automate [Pain Point] in [Industry]”)
- Align directly with mid-funnel discovery intent
- Excellent for product-led SEO when structured around workflows
- Customer Case Studies with SEO Layers
- Optimize for "[industry] + results" or "[tool] + use case" keywords
- Blend social proof with organic discoverability
- Evergreen Technical Tutorials (E.g., “How to Set Up SAML SSO in Your App”)
- Long-tail traffic magnets
- Low maintenance, high durability in rankings
- Ideal for building topical authority in dev-centric SaaS
💡 Strategy Tip: Use these high-ROI formats to prioritize content net new creation or post-audit rewrites. Tag them for deeper funnel alignment during your audit phase.
What’s the benchmark traffic for “successful” SaaS content?
There’s no universal traffic number that defines "success", but in SaaS, traffic should correlate with discoverability, product relevance, and conversion opportunity. Use the following benchmarks to assess whether a page is underperforming or worth scaling.
SaaS Content Traffic Benchmarks (Based on 90-Day Rolling Averages)
- Blog Posts (TOFU/Evergreen):
- Benchmark: 300–800 organic sessions per post
- Top-tier posts can exceed 1,500–3,000 if targeting high-volume queries
- Flag for review: <100 organic sessions in 90 days
- Feature Landing Pages:
- Benchmark: 200–600 sessions (branded + non-branded combined)
- Product-led SEO pages often see smaller volumes but higher conversion rates
- Comparison/BOFU Pages:
- Benchmark: 100–400 sessions
- These pages convert better even at lower traffic; prioritize intent match over volume
- Definition / “What Is” Content:
- Benchmark: 500–2,000+ sessions
- Great for backlinks, snippet wins, and topical authority
💡 SaaS Content “Traffic” Diagnostic Tip:If high-value content (BOFU, ICP-aligned) is under 150 sessions in 3 months despite ranking for 3+ keywords, it likely has title/intent mismatch or needs deeper optimization.
Turning Audits Into Scalable Strategy
This section introduces the strategy for embedding audits into quarterly ops cycles, using scoring templates, ownership workflows, and sprint planning to make content auditing a repeatable growth system.
How do you turn a one-time audit into a repeatable process?
To scale content performance, the audit can’t be a one-and-done project. It needs to evolve into a repeatable operational layer. This means building habits, templates, and cycles that connect audit insights directly to your publishing and optimization workflows.
Checklist: Turning an Audit Into a Repeatable Process
- Codify your audit framework: Use a consistent rubric (like the SaaS Content Pruning Matrix™) to score and prioritize content across SEO and business value.
- Choose your cadence: Run quarterly content audits to align with strategic planning cycles.
- Operationalize in tools: Use Airtable or Notion to track each piece of content's status, audit score, next action, and owner. Trello works well for smaller teams needing kanban-style visibility.
- Automate signal detection: Set up Google Looker Studio or GA4 dashboards to flag decaying posts and rank drops automatically.
- Integrate into content calendar ops: Every update or net-new decision should map to audit results. Make it a rule: nothing gets published without audit alignment.
- Assign audit sprints: Designate one week per quarter to focus purely on audit-driven updates—no net-new content allowed.
What is the content lifecycle for SaaS blogs?
Every SaaS blog post goes through a six-stage content lifecycle, and audits help maximize the value extracted at each stage.
SaaS Blog Content Lifecycle:
- Ideation – Topics are mapped to product features, personas, and ICP pains.
- Creation – Drafting and optimizing using tools like Clearscope, Surfer, or ChatGPT + internal SME insights.
- Publishing & Distribution – Post goes live and is distributed via newsletter, social, syndication.
- Performance Window – Organic traction starts (~60–90 days in). Posts typically peak in impressions/CTR during this window.
- Decay & Cannibalization Risk – Without updates, posts lose rankings or get buried by competing assets.
- Audit & Refresh – Audit identifies content worth pruning, updating, or consolidating based on traffic, rankings, and conversion metrics.
💡 Why this matters: Without a lifecycle model, content ops drift toward volume over value. Embedding audits at stage 6 allows teams to recover decaying posts before they underperform, ensuring higher ROI per asset.
How can audits inform your future SEO or content strategy?
A content audit isn’t just a cleanup job, it’s a strategic intelligence tool. When integrated into planning, audits drive content prioritization, thematic expansion, and SEO alignment across quarters.
Here’s how audit findings inform future content strategy:
- Content gaps → Net-new roadmap: If high-converting queries appear in GSC but lack dedicated posts, those terms go to the “net-new” queue.
- Top-performers → Expansion plays: Pages with high engagement but limited keyword spread signal a fit for cluster expansion or internal linking hubs.
- Decaying assets → Refresh roadmap: Posts with high impressions but dropping CTRs (as seen in GA4 and GSC) become top refresh priorities.
- Cannibalization clusters → Consolidation planning: If two posts rank for the same term, audits help decide whether to merge or retarget one for distinct intent.
- Misaligned traffic → Messaging or ICP repositioning: If organic traffic is high but engagement is low, it often signals poor audience–content fit.
How do you integrate audits into quarterly content ops?
To embed audits into your quarterly ops without disrupting publishing velocity, they need to be scheduled, templatized, and cross-functional.
Use the if-this-then-that model below to align audit execution with quarterly content cycles:
Quarterly Content Audit Integration Model
- If you’re planning Q3 campaigns, → run the audit in Week 2 of Q2 to inform content themes and gaps.
- If you publish 5+ posts/month, → schedule an audit sprint every 90 days to flag decaying assets and update priorities.
- If you use Notion or Airtable for your calendar, → create a “Content Audit” tag/status field that flows into your backlog or calendar view.
- If your content team operates in sprints, → dedicate one sprint per quarter to 100% audit-driven updates (no net-new posts).
- If your Head of Content owns reporting, → automate an “Audit Brief” doc every quarter using GA4 + GSC + Ahrefs exports, then review at OKR kickoff.
What’s the ROI of recurring content audits for SaaS companies?
Recurring content audits deliver compound ROI, not just from revived blog posts, but from a more efficient, conversion-aligned content engine.
Here’s how recurring audits contribute to ROI:
ROI Channels from Ongoing Content Audits
- Traffic Uplift from Refreshes: Updated content regains lost rankings and CTR, often within 30–60 days.
- Pipeline Growth via Conversion Optimization: Audits surface high-traffic posts with weak CTAs. Minor tweaks to CTAs or offer placement can lead to major SQL lifts.
- Publishing Efficiency Gains: Fewer low-impact posts. Audits help teams publish 20–40% fewer pieces while driving more qualified traffic.
- Strategic Focus: Align content creation with business goals instead of chasing trends.
![How to Perform a Content Audit To Win Placements in SGE Results [2025]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/94xmaaw6/production/8da9daf6ad97f540344aac9cbd8926f62978aa56-1536x1024.png)




